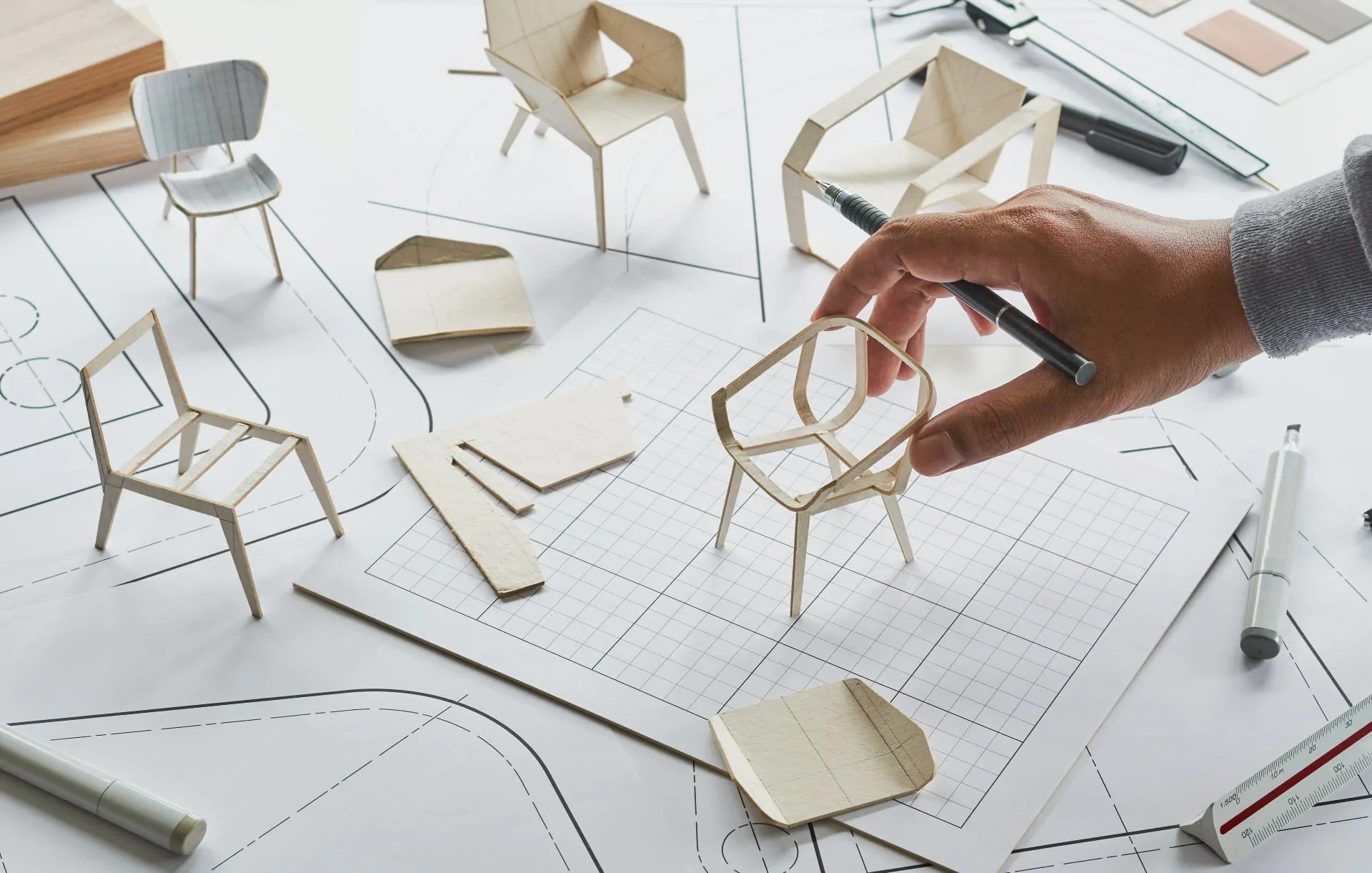
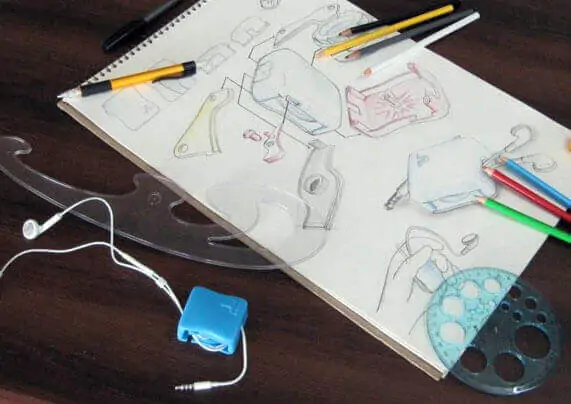
Even ancient craftsmen and innovators recognized the value of prototyping and product development in the process of creating new products. Before making the necessary adjustments to produce the principal artifacts in accordance with the blueprints, they developed crude but fully functional copies of their concepts.
As early and clearly as feasible in the project, features and functions must be identified. During the prototyping or product development stage, it will be examined to see if the potential product possesses all the specified qualities and traits. Things can be further optimized than originally planned, though, during this key stage. However, there is a chance that the designers will choose to forgo some features for a variety of reasons, including production viability and financial constraints.
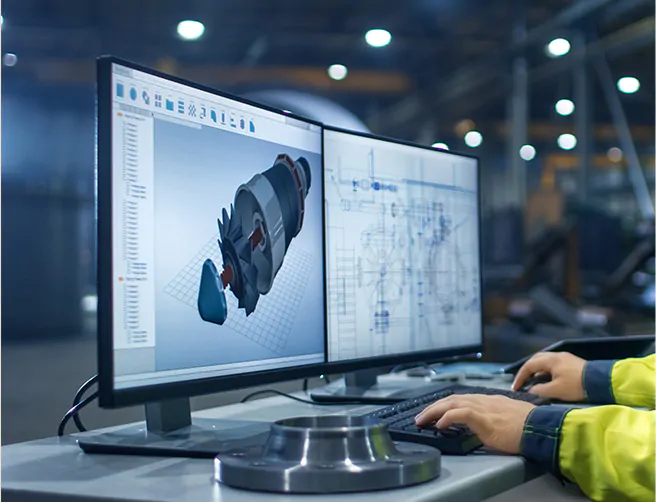
Although a product’s final version may differ slightly from the original concept, it must nonetheless satisfy the needs of its target audience. The prevalence of computer-aided design (CAD) tools utilized by CAD services professionals, engineers, and manufacturing specialists has made product development easier in today’s hardware & research development.
Which Prototyping Technique and How Much?
There is no simple solution for that. The cost is determined by a few elements, with the product development method being one of the most important. There are numerous possibilities, including:
-
-
-
- White model: a basic, non-operational visual depiction of a design made of modeling clay or solid construction. Less than a day may pass during the prototyping process. The additive manufacturing process of 3D printing is used to create prototypes with minimal functionality, fine details, and textures.
- A more accurate 3D printing technique that uses a UV laser and UV-curing resin is stereolithography (SLA). Due to the laser’s narrow focus width compared to its FDM (fused deposition modeling) counterpart’s larger nozzle size, precise prototyping is possible.
- SLS machines employ powdered materials to be melted, fused, or sintered using lasers of variable powers. These machines are on the more expensive end of 3D printing technology. The method may create precise prototypes with intricate geometry and interconnected parts.
- Micromachining is a subtractive manufacturing process that makes use of CNC and EDM machines (electrical discharge machining). A single piece of robust material, such as metal, is used to construct the prototype.
-
-
-
-
-
- Vacuum casting: Prototypes are used to create silicone molds. The identical parts are then produced using the molds. The hardware of manufacturing quality is the end outcome. There is also the option of metal casting.
-
-
-
-
-
- Urethane, soft, or full production injection molding tools are examples of prototype tooling. Hard-tooled plastic parts are produced by prototype tooling, while soft plastic is better for initial samples, and full production is suited for final prototypes with stricter tolerances.
-
-
In contrast to subtractive prototyping, which adds material, additive prototyping removes material. Both can be employed in production. A hybrid strategy exists as well, which makes use of both approaches, like in the polishing of a 3D printed item. Both the additive and subtractive methods have affordable costs, but only for limited volume prototyping, particularly when the product needs specific components that are difficult to create or mass-produce.
Why Build Hardware Prototypes?
Building prototypes enables the design and engineering team to gain additional insight into the functionality of the product before it is delivered to the manufacturing line for electrical devices (or any other sort, for that matter). The team learns important lessons and has a better knowledge of potential problems as well as the product’s advantages and disadvantages in everyday use, whether the prototype succeeds, or functions as expected. If more improvement is needed, it can be suggested by the team to further lower the risk of failure.
When created using CAD, product development may appear attractive on a computer screen. However, it is impossible to predict whether the product will function in a real-world usage setting until the digital concept is translated into a physical artifact. The product development costs include “looks-like” and “final product” versions, but this stage is necessary. It is preferable to find design defects before production rather than having to start over after a product has been released to the market.
Cost for Hardware Prototyping
Once more, it’s a question with numerous possible answers. When you are thinking about a specific product, you get precise replies. The good news is that compared to industrial and medical devices, consumer electronics items categorically cost less and prototype more quickly.
Because each product has difficulties in terms of the production budget, the variety in prototyping prices might be substantial. A professionally constructed hardware prototype of a consumer electronics product will range in price from $300 to as much as $100,000, to put it simply.
What is the Hourly Rate for product development?
Most prototype makers would consider the level of difficulty before charging on a per-project basis. Very few would utilize an hourly rate to estimate the total cost. The ideal hourly pay for a design firm in the US is between $50 and $200. In addition to staff providing administrative assistance, the company often includes engineers in the fields of software, electronics, and mechanical engineering.
Should You Hire Individuals or a Design Firm?
Depending on who you hire to build the prototype, there can be a significant difference in completion time, cost, and quality.
When you’re not yet familiar with product development, hire a hardware development company. You don’t have a network of industry experts and putting together a team would take a lot of time. When money is not concerned, consumer electronics prototypes can run into the five digits. Throughout the procedure, numerous iterations can be necessary.
When a prompt completion time is required, typically, a design firm’s expert staff can complete the task more quickly. An established business most likely has links with reliable component suppliers in addition to its own skill pool.
When software takes center stage, hardware prototypes can also refer to a product’s outside casing. It is recommended to engage a design company to build the physical prototype when your major line of business is the creation of software so that you may concentrate on your main line of business.
Here are several businesses in the United States and Canada listed by Washington, DC-based market research company Clutch so you can get a decent idea of how much a hardware development company charges for prototyping services.
How can Monarch Innovation help?
The independent experts at Monarch Innovation have the skills and connections to assist you with 3D modeling and connect you with the manufacturing, rapid prototyping, and 3D printing services you require to get your product to market. Contacting us will help you save time! Bring it to your favorite manufacturer. Get a price or see how it operates.