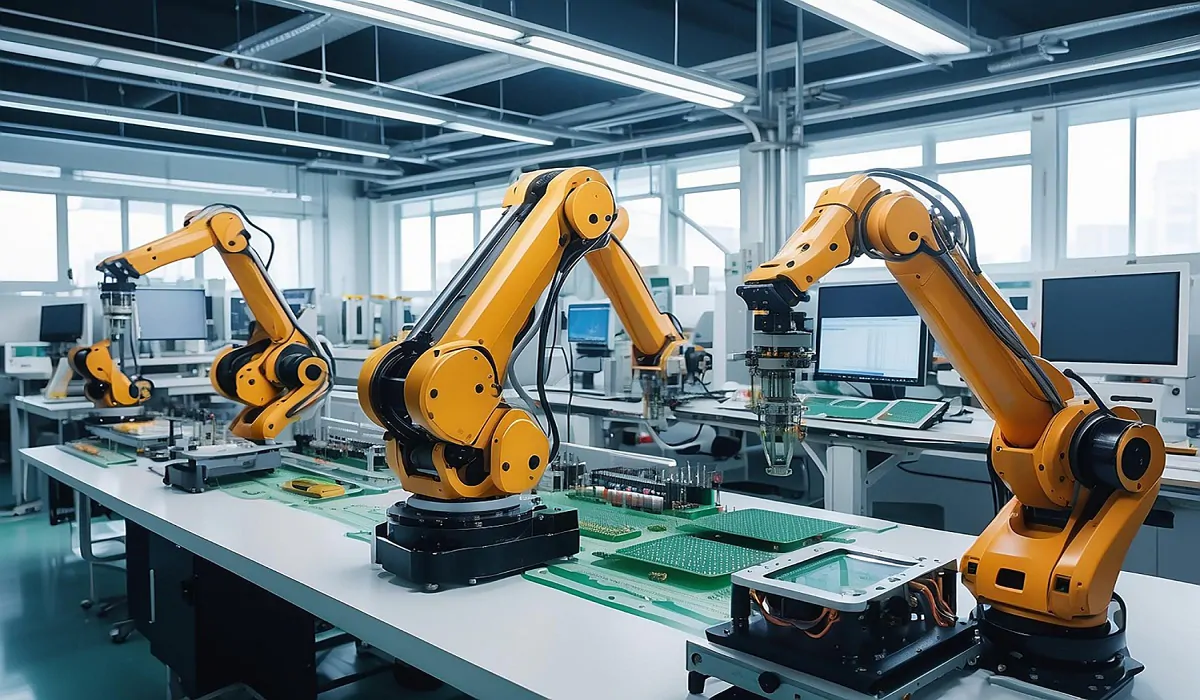
In an era of rapid technological advancement, robotics engineering stands out as a field with immense potential to revolutionize industries and enhance our daily lives. Robots have become essential tools across various sectors, including healthcare, manufacturing, space exploration, and entertainment. This blog aims to explore the future of robotics engineering by defining the field, highlighting its priorities, discussing different types of robots, and examining its potential to transform industries.
What is Robotics Engineering?
At its core, robotics engineering is a specialized branch of engineering that focuses on designing, constructing, and programming robots. These machines are engineered to perform a wide range of tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. Robotic engineering integrates principles from mechanical, electrical, and computer engineering to create sophisticated robotic systems capable of interacting with their environment and executing complex operations.
Key Aspects of Robotics Engineering
Robotics engineering encompasses the design, development, programming, and integration of robots. It involves:
- Design and Development: Robotics engineers are involved in crafting the physical structure of robots, including components such as actuators (motors), sensors, and control mechanisms. This phase is crucial as it determines the robot’s capabilities and functionalities.
- Programming and Algorithms: The software aspect of robotics is vital for enabling robots to perceive their surroundings, make decisions, and execute tasks. Advanced algorithms, often incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning, empower robots to adapt and learn from their interactions.
- Integration: Successful robotics projects hinge on seamlessly integrating mechanical, electrical, and software components. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that robots operate efficiently and effectively in diverse environments, fulfilling their intended roles.

What are Robotics and Automation?
While robotics focuses on creating and using robots, automation involves using technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. Automation includes robots but also encompasses other technologies like computer software and control systems. Robotics enhances automation by providing the physical presence needed to perform tasks in various environments. Together, they transform industries by increasing efficiency, precision, and safety. For example, robots in manufacturing automate assembly lines, leading to faster production rates and higher-quality products.
Types of Robots
Robots come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific tasks and environments. Here are some common types:
- Industrial Robots: Used in manufacturing for tasks like welding, painting, assembling, and material handling. These robots are accurate, fast, and can operate in hazardous environments.
- Service Robots: Assist humans by providing services in homes and businesses. Examples include robotic vacuum cleaners, lawnmowers, and healthcare robots used in surgical procedures.
- Mobile Robots: Navigate through spaces using wheels, tracks, or legs. They are used in transportation (e.g., self-driving vehicles), space exploration, and as robotic pets.
- Humanoid Robots: Designed to mimic human movements and interactions. They are used in scientific research, customer service, and as personal assistants.
- Autonomous Robots: Operate independently using sensors and artificial intelligence. Examples include drones for surveillance, underwater vehicles for exploration, and self-driving cars.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Work alongside humans in shared environments. They are equipped with sensors and safety features to minimize accidents and injuries, commonly used in industries requiring human-robot interaction.
- Medical Robots: Used in healthcare for tasks like surgery (e.g., Da Vinci Surgical Robot), physical therapy, and diagnostics. They improve the precision and success rates of medical procedures.
Conclusion
Robotics engineering is a dynamic and evolving field with the potential to significantly impact various aspects of our lives. From automating factory processes to developing advanced medical devices and artificial limbs, robots are opening new doors that are reshaping our world. As technology continues to advance, the integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced sensing technologies will make robots smarter and more efficient.
Join us in exploring the limitless possibilities of robotics engineering at Getra Innovation, where innovation meets excellence.
Frequently Ask Questions
Which Language is used in robotic engineering?
In robotics engineering, the languages commonly used include C++, Python, and MATLAB, among others. These languages are chosen for their ability to handle tasks such as programming robot controllers, implementing algorithms for navigation and perception, and interfacing with sensors and actuators effectively.
What career opportunities are available for robotics engineers?
Robotics engineers can work in various industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, and defence, designing and developing robotic systems.
What is the future of Robotics?
The future of Robotics Engineering is promising, with advancements in AI, machine learning, and sensor technology driving innovation. Expect to see more sophisticated robots with enhanced capabilities in various sectors, including healthcare, agriculture, logistics, and everyday life.
What are the different types of robots in robotics engineering?
Robots in robotics engineering can be categorized into industrial robots, mobile robots, humanoid robots, and collaborative robots, among others.
What skills are needed for a career in Robotics?
Key skills for robotics engineering include proficiency in programming, mechanical design, electronics, and problem-solving abilities.
What is the role of artificial intelligence in robotics engineering?
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in robotics engineering by enabling robots to perceive their environment, make decisions, and adapt to changing situations.