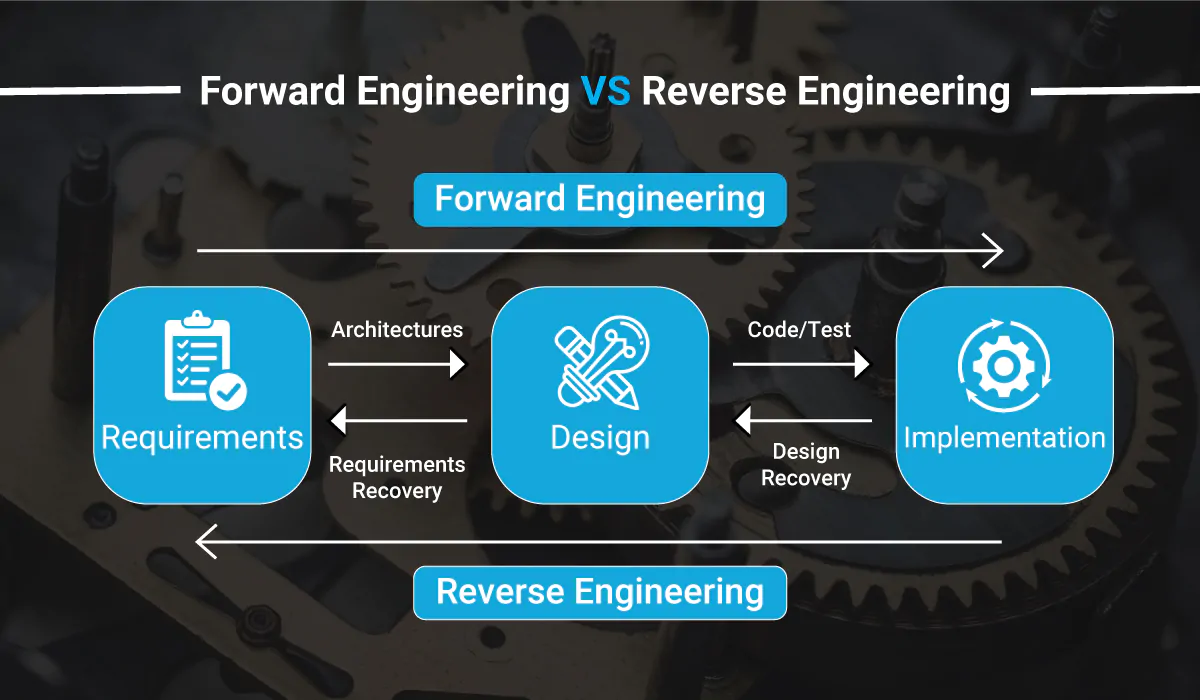
In product development, two different approaches are commonly used: forward engineering and reverse engineering. While forward engineering involves creating new products from scratch, reverse engineering involves analyzing and replicating existing products. This blog will explore the key differences between forward engineering and reverse engineering, and the various applications of both approaches.
Forward engineering and reverse engineering are two different approaches used in product development. While forward engineering involves creating new products from scratch, reverse engineering involves analyzing and replicating existing products. Each approach has its advantages and disadvantages, and the decision to use one or the other depends on the specific needs of a project. Now, we will explore the key differences between forward engineering and reverse engineering in more detail.
Forward Engineering
Forward engineering is the traditional approach to product development, in which designers and engineers start with a concept or idea and work through a series of steps to create a final product. This process typically involves several stages, including ideation, prototyping, testing, and refinement. In forward engineering, the design and development process starts with a clear understanding of the requirements and specifications of the product. Designers and engineers then work together to develop a detailed plan for the product, which includes defining the materials, manufacturing processes, and assembly procedures that will be used.
Once the plan is in place, the product is then prototyped and tested to ensure that it meets all the necessary requirements. Feedback from testing is used to refine the design and improve the product until it is ready for production. Forward engineering is commonly used in product development for a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, electronics, and software. The key advantage of forward engineering is that it allows designers and engineers to create products that are customized to meet specific requirements and to optimize the design for the intended purpose.
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering, on the other hand, involves the analysis and replication of existing products. This process is often used when there is a need to reproduce a product that is no longer available or to modify an existing product to improve its performance. Reverse engineering typically involves several stages, including disassembly, measurement, analysis, and replication. The first step in reverse engineering is to disassemble the product and analyze its components to understand how it was designed and manufactured.
Once the product has been disassembled, measurements are taken of each component and its relationship to other parts of the product. This information is then used to create a 3D model of the product, which can be used to create new designs or modify the existing product. Reverse engineering is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing. The key advantage of reverse engineering is that it allows designers and engineers to understand the intricacies of an existing product and to make improvements or modifications based on that knowledge.
Comparison
- The main difference between forward engineering and reverse engineering is the starting point of the design process. In forward engineering, the design process starts with a concept or idea and moves towards a finished product, while in reverse engineering, the process starts with a finished product and moves towards a new design.
- Another key difference between forward engineering and reverse engineering is the level of control that designers and engineers have over the design process. In forward engineering, designers and engineers have complete control over the design and development of the product, while in reverse engineering, the design process is limited by the existing product.
- Finally, the level of uncertainty is also a key difference between forward engineering and reverse engineering. In forward engineering, there is typically a higher level of uncertainty, as designers and engineers are working with a new concept or idea. In reverse engineering, there is less uncertainty, as designers and engineers are working with an existing product that has already been proven to work.
Difference between Forward Engineering and Reverse Engineering.
|
Key Points |
Forward Engineering |
Reverse Engineering |
|
Definition |
Forward Engineering is the process of creating a new system from scratch. |
Reverse Engineering is the process of analyzing an existing system to understand its design and functionality. |
|
Starting Point |
Forward Engineering begins with requirements analysis, i.e., identifying the needs and expectations of stakeholders for the system. |
Reverse Engineering begins with the analysis of an existing system to understand its design and functionality. |
|
Output |
Forward Engineering produces a new system that meets the specified requirements. |
Reverse Engineering produces a system model that describes the existing system. |
|
Decision Making |
In Forward Engineering, design decisions are made upfront based on the requirements and objectives of the system. |
In Reverse Engineering, decisions are made after analyzing the existing system to determine how it works and what changes may be necessary. |
|
Focus |
Forward Engineering focuses on creating a new system that meets future requirements and addresses identified needs. |
Reverse Engineering focuses on understanding and analyzing an existing system to determine how it works and what changes may be necessary. |
|
Approach |
Forward Engineering follows a structured approach, involving the identification of requirements, system design, implementation, testing, and validation. |
Reverse Engineering may follow an ad-hoc approach, where the analyst determines the best course of action based on the information available. |
|
Level of Detail |
Forward Engineering involves high-level abstraction, focusing on the overall system design and functionality. |
Reverse Engineering involves low-level details, focusing on the specific components and mechanisms of the existing system. |
|
Testing and Validation |
In Forward Engineering, testing, and validation are essential to ensure that the new system meets the specified requirements and works as intended. |
In Reverse Engineering, testing and validation may be necessary to confirm the accuracy of the system model and identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies. |
|
Examples |
Examples of Forward Engineering include software development, building a bridge, or designing a new product. |
Examples of Reverse Engineering include analyzing malware to understand its behavior and reverse engineering a competitor’s product to understand its design and functionality. |
Types of Reverse Engineering and Forward engineering
There are several types of reverse engineering and forward engineering methods used in various industries for product development. Let’s look at some of the most common types:
Types of Reverse Engineering:
- 3D Scanning: This method involves using a 3D scanner to create a digital model of an existing object. The scanner captures the object’s geometry and creates a 3D point cloud that can be used to create a CAD model.
- Photogrammetry: Photogrammetry is a technique that uses photographs to create a 3D model. This method involves taking multiple photographs of an object from different angles and then using software to create a 3D model from the images.
- CT Scanning: CT scanning is a method that uses X-rays to create a 3D image of an object’s internal structure. This method is often used in the medical industry to create detailed images of bones and other internal structures.
Types of Forward Engineering:
- Conceptual Design: This involves the creation of initial concepts and sketches to define the overall design of a product.
- Detailed Design: Once the conceptual design is approved, detailed design work begins. This involves creating detailed drawings, specifications, and engineering documents that provide all the information needed to manufacture the product.
- Prototyping: Prototyping involves creating a physical model of the product to test its functionality and design. This stage may involve multiple iterations until a final prototype is approved for production.
- Manufacturing: Once the design and prototype are finalized, the manufacturing process begins. This involves producing the product on a larger scale, typically using specialized equipment and processes.
It’s important to note that reverse engineering and forward engineering are often used in conjunction with each other. For example, a product may be reverse-engineered to create a digital model, which is then used in the forward engineering process to refine the design and create a final product.
In conclusion,
Both forward engineering and reverse engineering have their unique roles in the product development process. Forward engineering helps in creating new products from scratch, while reverse engineering assists in improving existing products by analyzing and reproducing them. At Getra Innovation, we understand the importance of both types of engineering in product development and offer services in both areas, including 3D reverse engineering and forward engineering for industrial product design. Our team of experts provides innovative and effective solutions to meet our client’s needs, whether it is to create a new product or improve an existing one. Contact us to learn more about how we can help you with your product development needs.